Clinical results & Publications
Sleep staging in the ICU with heart rate variability and breathing signals. An exploratory cross-sectional study using deep neural networks
The cardiovascular and respiratory networks encode sleep state information, which, together with artificial intelligence methods, can be utilized to measure sleep state in the ICU.
High prevalence of sleep disordered breathing in the intensive care unit — a cross sectional study
Undiagnosed sleep-disordered breathing is common in the ICU and is associated with a substantial burden of hypoxia and periodic breathing. MGH study demonstrates the potential of detecting sleep-disordered breathing using Airgo™, without the need for formal polysomnography.
Editorial: Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS). What's new?
This Frontiers in Medicine Editorial confirms that OSAS is a hot topic, and that Airgo™ is a reliable tool for screening suspected OSAS patients.
This special issue discusses several of the “unmet needs” in OSAS diagnosis and treatment, and underlines the importance of assessing the risk of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome, as this syndrome is linked with a high risk of hypertension, cardiovascular diseases, daytime sleepiness, home, and work-related accidents, and a consequent worsening of life quality.
Authors:
Barbara Ruaro1, Elisa Baratella, Marco Confalonieri1, Caterina Antonaglia and Francesco Salton
Front. Med., 15 September 2022
Airgo™ is a reliable tool to screen patients with suspected sleep respiratory disorders
The use of Airgo™ as a screening tool is only a part of the rich, informative signal processing of the device. The visualization of vectors recorded overnight is far more informative.
Airgo™ is a reliable tool to screen patients with suspected sleep respiratory disorders, well tolerated by the patient based on totally automatic analysis and reporting system, leading to more efficient use of doctor’s and clinician’s time and resources and extending the opportunity to diagnose more possible candidates for treatment.
Authors:
Alberto Braghiroli, David Kuller, Massimo Godio, Fabio Rossato, Carlo Sacco and Elisa Morrone
Front. Med., 01 July 2022
Peer reviewed publications
Comparison of Airgo™ and metabolic cart signals.
Comparison between the Airgo™ Device and a Metabolic Cart during Rest and Exercise
A new study by the Politecnico di Milano and Ospedale Santa Croce e Carle of Cuneo highlights Airgo™'s precision at monitoring respiratory rate, tidal volume and minute ventilation at rest, comparing results to gold standard metabolic cart.
Authors:
Andrea Antonelli, Dario Guilizzoni, Alessandra Angelucci, Giulio Melloni, Federico Mazza, Alessia Stanzi, Massimiliano Venturino, David Kuller and Andrea Aliverti
Sensors 2020, 20(14), 3943;
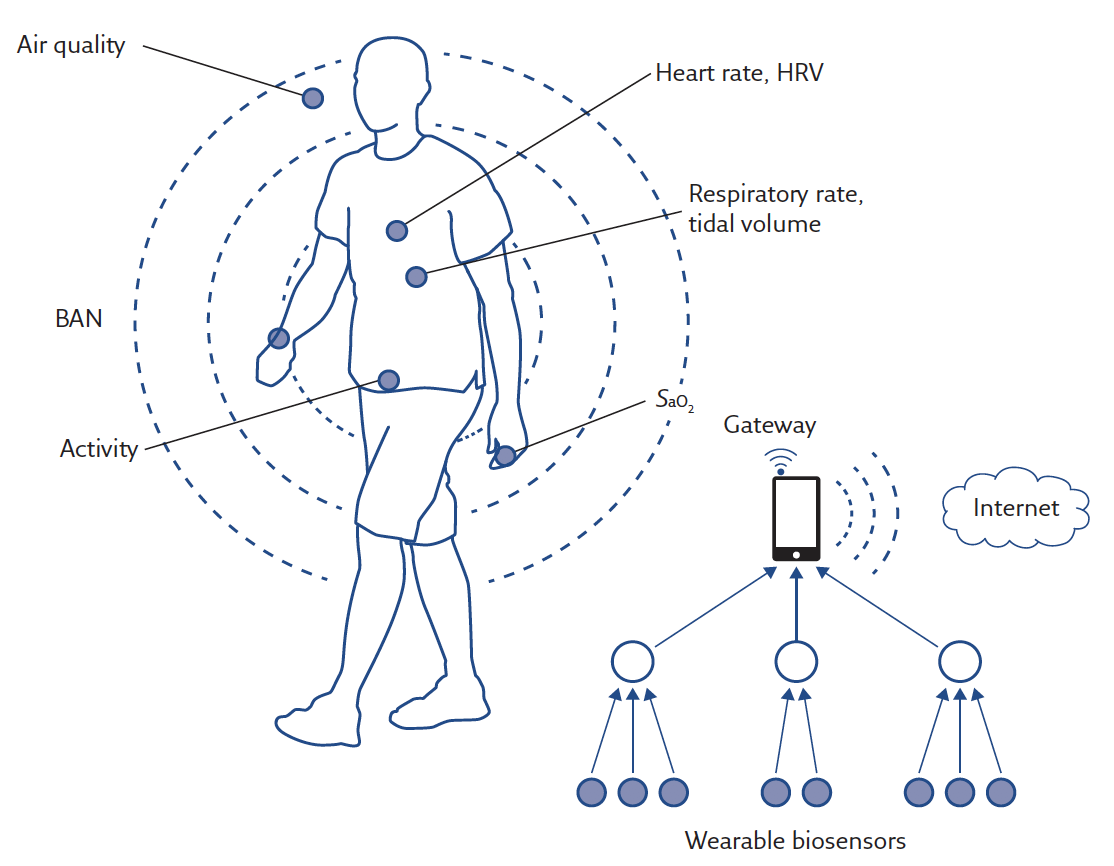
Architecture of a patient monitoring system using wearable sensors. HRV: heart rate variability; SaO2: arterial oxygen saturation.
Wearable technology: role in respiratory health and disease
In this review, four main areas of interest for respiratory healthcare are described: pulse oximetry, pulmonary ventilation, activity tracking and air quality assessment. Although several issues still need to be solved, smart wearable technologies will provide unique opportunities for the future or personalised respiratory medicine.
Author:
Andrea Aliverti
Breathe (Sheff). 2017 Jun;13(2):e27-e36.
A home telemedicine system for continuous respiratory monitoring
Airgo respiratory monitor takes part in successful 5G telemonitoring trial in Italy with Vodafone and the Politecnico di Milano.
The published article discusses the continuous home telemonitoring system for chronic respiratory patients using 5G connectivity developed in partnership with Vodafone as a part of the 5G Trial in Milan established by the Italian Ministry of Economic Development. The system features Airgo™, a wearable respiratory and activity monitor, an environmental sensor and a pulse oximeter sending the data through a 5G router to a Multi-Edge Computing server, incorporated in the Vodafone 5G infrastructure, where they are stored and accessible for visualization.
Authors:
Alessandra Angelucci, David Kuller, Andrea Aliverti
IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2020 Jul 28
A Multimodal Wearable System for Continuous and Real-Time Breathing Pattern Monitoring During Daily Activity
This study aims to understand breathing patterns during daily activities by developing a wearable respiratory and activity monitoring (WRAM) system.
Results: The advantage of the proposed HHC method is evaluated by comparing the average accuracy (97.22%) and predictive time (0.0094 s) with machine learning and deep learning approaches.
Authors:
Wen Qi, Andrea Aliverti
IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2020 Aug; 24(8):2199-2207.
Telemonitoring system with a two-hop data transmission architecture.
Telemonitoring systems for respiratory patients: technological aspects
This review introduces the reader to the available technologies in the field of telemonitoring, with focus on respiratory patients. In the materials and methods section, a general structure of telemonitoring systems for respiratory patients is presented and the sensors of interest are illustrated, i.e., respiratory monitors (wearable and non-wearable), activity trackers, pulse oximeters, environmental monitors and other sensors of physiological variables. Afterwards, the most common communication protocols are briefly introduced.
Authors:
Alessandra Angelucci, Andrea Aliverti
Pulmonology. 2020 Jul-Aug;26(4):221-232.
Clinical abstracts
Validation study of a new analysis software to screen sleep respiratory disorders
Methods: Airgo™ is an innovative device consisting of a comfortable elastic band and a small box containing a microprocessor and 3 accelerometers. It is positioned over the lower chest and calculates tidal volume and respiratory rate, detecting respiratory events during sleep and body position. We tested the device in 120 consecutive pts (21 F) simultaneously undergoing a CRM (Nox T3). The trend of AHI in the deciles 30-50% is the best descriptor of respiratory disorder.
Results: The mean age of pts (± SD) is 55.7±13 yrs, BMI 27.8±4.3 kg/m2, AHI 22±22 events/hr. Airgo classified properly 27 severe OSA pts, 16 postural OSA (pOSA), 16/19 non-OSA pts (3 FP), 35/40 mild-to-moderate OSA (3 scored severe and 2 FN) and 14/16 pts (2 FN) with irregular breathing of non-OSA origin. In the OSA group the overall sensitivity is 97.5%, with 94% positive predictive value and 89% negative predictive value. The advanced visualization technique allows a refinement of analysis, correcting for false negatives and defining breathing patterns useful for phenotyping patients.
Authors:
A. Braghiroli, C. Sacco, A. Giordano, M. Godio, F. Rossato, S. Rossi, S. Carli, B. Balbi, D. Kuller, E. Morrone
ERS 2021 - Poster presentation
Sleep Staging with a Wearable Respiratory Signal Adapted to an Inductance Plethysmography-based Deep Learning Model
Electroencephalography (EEG) is used as the main signal to stage sleep. However, a more practical and patient-friendly assessment of sleep is in demand. Here, we assess the efficacy of a wearable respiratory device called AirGo(MyAirLLC).
Conclusions: Transfer learning provides a model to stage sleep with a wearable respiratory device.
• The sleep stage-prediction model’s performance and agreement with human expert is moderate to substantial.
• More wearable device data and hyperparameter tuning might further increase performance.
• Model can help with more practical and patientfriendly assessment of sleep.
Authors:
Wolfgang Ganglberger, Haoqi Sun, Ryan A. Tesh, Ezhil Panneerselvam, Michael J. Leone, Luis Paixao, Syed Abdul Qader Quadri, Robert J. Thomas, David Kuller, M. Brandon Westover
IEEE conference on AI in medicine in Berlin, July 2020 - Poster presentation
Validation study of a new analysis software to screen sleep respiratory disorders
Airgo™ is a promising screening tool to stratify the occurrence of respiratory sleep disorder, identifying pts with severe OSA, pts with postural OSA, pts with irregular breathing and with mild-to-moderate disease providing data visualization useful for phenotyping patients.
Authors:
A. Braghiroli, C. Sacco, A. Giordano, M. Godio, F. Rossato, S. Rossi, S. Carli, B. Balbi, D. Kuller, E. Morrone
Presented at European Respiratory Society (ERS) International Congress 06/09/2021;
Validation study of an innovative device to screen sleep respiratory disorders
A simple and reliable screening tool is a real need to couple the epidemiology of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) with the resources available in sleep laboratories, particularly in patients with OSA and comorbidities who often do not have symptoms (i.e.: somnolence).
Conclusions: Airgo is a promising screening tool to stratify the occurrence of respiratory sleep disorders, identifying pts with severe OSA, pts without RBD, pts with irregular breathing and with mild-to-moderate disease. The performance is excellent in discriminating postural OSA.
Authors:
A. Braghiroli, C. Sacco, A. Giordano, M. Godio, F. Rossato, S. Rossi, S. Carli, D. Kuller, B. Balbi, E. Morrone
ERS 2020 - Poster presentation
Validation study of the AirGo™ device for the continuous monitoring of respiratory function
Standard functional respiratory tests require patient cooperation and do not allow continuous and accurate assessment of respiratory function under natural physiological conditions. AirGo™ is a non-invasive wearable device that continuously records breath dynamics during sleep and daily activity.
Authors:
A. Antonelli, A. Stanzi, F. Mazza, M. Venturino, P. Noceti, D. Guilizzoni, A. Aliverti and G. Melloni
ERS 2018 - Poster presentation